Taiwan Can Help - National Health Insurance’s Contribution in Combating COVID-19
I. National Health Insurance in Taiwan
Taiwan's National Health Insurance (NHI) program has launched since 1995 and continues to receive international recognition. According to Numbeo, a global data website, Taiwan has ranked first in the world for four consecutive years in the 2022 Health Care Index. Additionally, in Bloomberg's January 2022 COVID Resilience Ranking, which evaluates countries based on indicators such as vaccine coverage, cross-border virus control, and medical quality, Taiwan ranked eighth in the world. During the COVID-19 pandemic, NHI has played a crucial role in disease prevention efforts.
The features and role in combating COVID-19 are as follows:
(I) Single-payer System
The government launched National Health Insurance in 1995, combining medical benefits of various insurances to form a single insurer— National Health Insurance Administration (NHIA). The regular NHI premiums are calculated based on the insured’s monthly salary, and are shared by the insured, the employer, and the government. The insurance premium and copayment for the disadvantaged groups are subsidized or reduced by the government. Because of the single insurer system, the policies on combating COVID-19 of NHI can benefit the people and the medical profession of Taiwan.
(II) Comprehensive Medical Coverage
Taiwan’s National Health Insurance provides comprehensive medical care, including outpatient care, inpatient care, dental care, Chinese medicine and prescription drugs. NHI provides comprehensive medical coverage for people, so they can feel free to seek medical treatment and do not need to worry about medical expenses.
(III) Easy Access to Healthcare
NHI has contracted with about 91.9% of medical institutions nationwide (100% of hospitals, 91.7% of primary clinics, and 81.5% of pharmacies).People can go to medical institutions freely and pay only a fixed amount copayment at the time of medical service with the rest of medical cost covered by the NHI. In Taiwan, the average number of medical visits per person per year is about 14.2 times. Taiwan’s high-accessibility and low-copayment condition makes people habitually seek medical services when they are not feeling well. Thus, during the times of the epidemic, the medical profession can easily track or reach potential patients or patients with mild symptoms, which is very helpful in fighting against the pandemic.
(IV) Digitalization of Medical Information
The hospital claims submission and payment reimbursement system are fully automated. The computer automatically examines the medical claims of medical institutions to increase efficiency, and also makes Taiwan's health insurance administrative cost reach the world's lowest (less than 1% of medical expenses). On the network system, a closed exclusive network, virtual private network (VPN), is used for data security. During the times of the COVID-19 pandemic, real-time sharing of medical information such as travel history, contact history and medical history is important to assist medical staff to discover and trace patients.
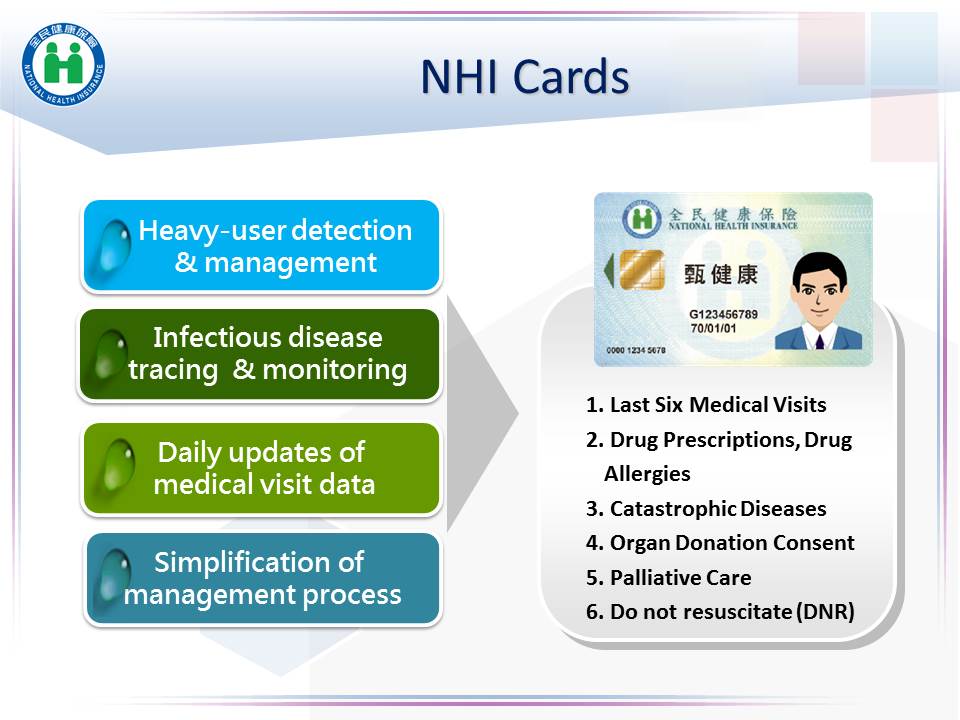
(V) IC-chipped NHI Card
The NHIA uses IC chip cards as insurance certificates, which can provide people with multiple smart functions. The health insurance card is an important link between the patient and the medical institution. The doctor can quickly obtain the patient's recent medical information, and can also be used to track the patient during epidemic outbreaks, such as the SARS in 2003 and the COVID-19 in 2020. The use of NHI card allows suspected cases to be tracked and detected in real time, which is helpful for epidemic prevention.
(VI) Promoting Referral System
In order to improve the quality of medical care, we also promote a tiered medical system. In addition to strengthening the service capacity of primary-level medical institutions, and raising the hospital's payment for treating critical diseases, the NHIA also builds a vertical integrated strategic alliance between hospitals and clinics. Large-scale hospital takes the lead in vertically integrated strategic alliances with neighboring primary-level medical institutions, and establishes a cooperative channel for transferring patients upstream or downstream. People can get medical care through tiered medical system, which can avoid the cluster infections caused by the influx of patients into the hospital.
(Ⅶ) International video conferences
1. iHEA Taiwan Session online conference:
The International Health Economics Association (iHEA) and invited Dr. Po-Chang Lee, Director General of the National Health Insurance Administration to speak on “How the IT System of National Health Insurance Plays a Role in Fighting COVID-19” during the 2021 iHEA Congress pre-session on July 7th 2021. This session explored how Taiwan has fought against the pandemic by the application of the information Technology on Taiwan's National Health Insurance, such as using NHI Express APP as an important tool for epidemic control, strengthening telemedicine services to reduce contact and develop digital vaccination certificates for the future use. The presentation has won the recognitions of the conference panelists and the audiences. More than 100 global health economic experts and scholars has participated online.
2. Taiwan and Philippine Joint Conference on How National Health Insurance Systems Has Responded to COVID-19:
By sharing the NHIA’s experiences of combating COVID-19, Taiwan's soft power in terms of medicine and public health has been demonstrated. Taiwan’s achievements in pandemic prevention has received international recognitions, and presented a new paradigm for other countries, where Representative Michael Pei-yung Hsu of Taipei Economic and Cultural Office in the Philippines acted as moderator, and the NHIA shared Taiwan’s experience on pandemic prevention policies. Meanwhile, Dr. Art Alcantara, Acting Chief Information Officer of the Philippines Health Insurance Corporation (PhilHealth) shared how the Philippines health insurance system has responded to the COVID-19 pandemic.
3. Taiwan and Thailand Joint Conference on How Health Insurance Systems Has Responded to COVID-19:
The Webinar was held on 16 December 2020, with support and assistance from the H. E. Ambassador Dr. Ying-Yuan Lee and Ms. Wilailuk Wisasa, the Acting Director of Bureau of International Affairs of Thailand National Health Security Office (NHSO), to share experiences on combating COVID-19, In addition to the National Health Insurance Administration (NHIA) sharing its pandemic prevention policies, Dr. Jung-Hsien Chiang, Professor of the National Cheng Kung University (NCKU), also shared their experiences on how medical institutions apply AI technology to add further value to pandemic prevention. The online audience from academia and medical institutions also joined the Webinar, gaining fruitful exchanges.
II. Promoting Digital Health
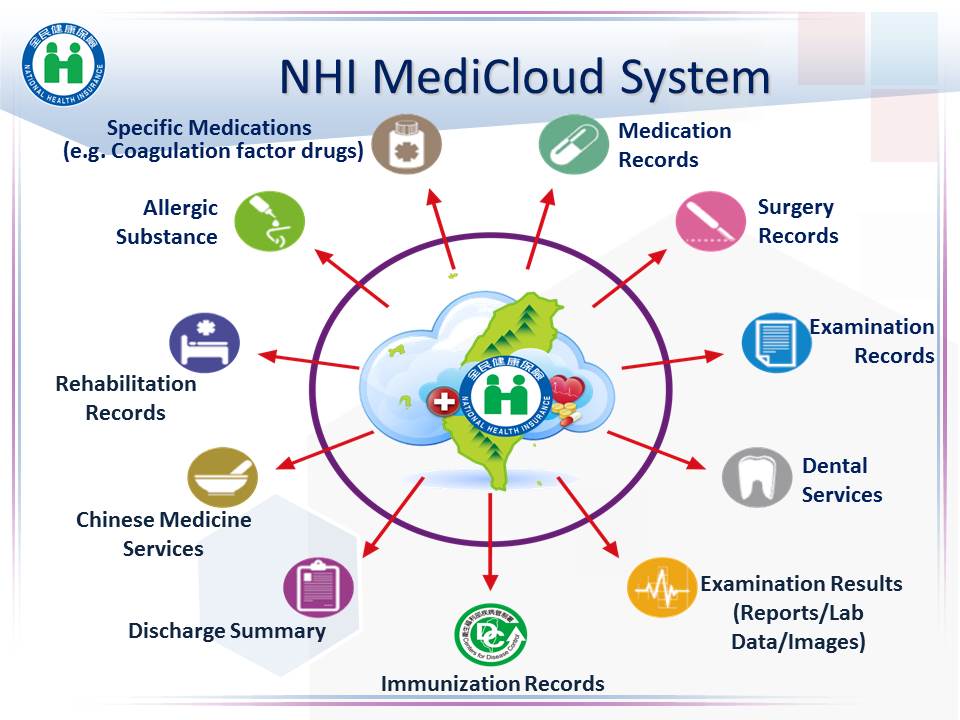
(I) NHI MediCloud System Assists in Fighting COVID-19
Through the "NHI MediCloud System", the medical information scattered in different hospitals and clinics across hospitals, counties and cities, regardless of holidays and day and night can be shared effectively. In 2013, the NHIA completed the patient-centered NHI PharmaCloud System. The NHIA upgraded the NHI PharmaCloud System to “NHI MediCloud System” in 2016 based on users’ feedback and clinical needs. NHI MediCloud system not only includes medication records but also includes other information like surgical records, examination records and results, dental care records, discharge summary, Chinese medicine records, rehabilitation records, history of allergy, specific drugs, and immunization records. Starting on 2018, the NHIA also encouraged hospitals to upload patients' medical images, including CT, MRI, ultrasound, gastroscopy, colonoscopy and X-Ray images, so that the images can be retrieved through the NHI MediCloud System by other hospitals or clinics.
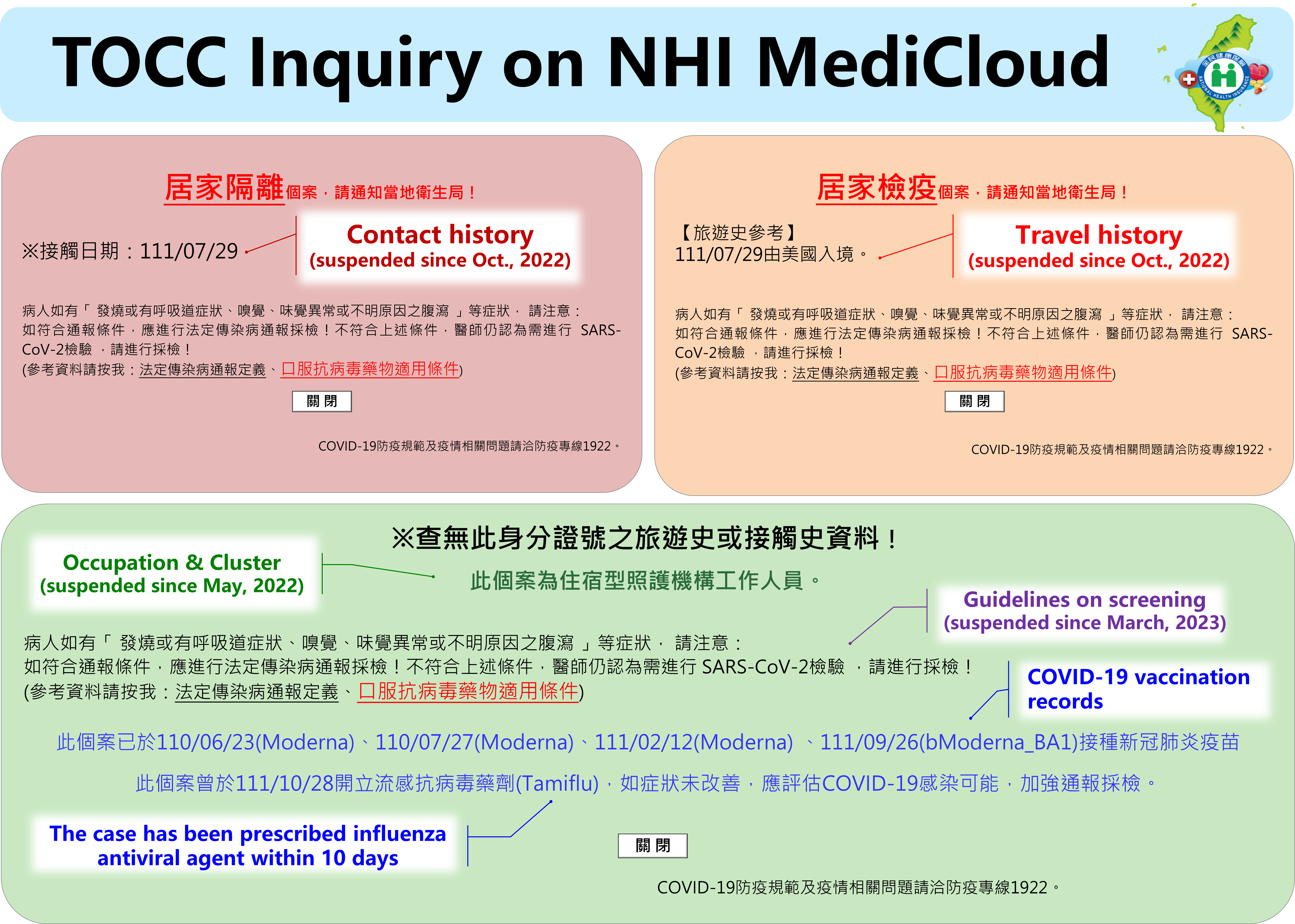
In the early stage of the outbreak of COVID-19, in order to effectively avoid the flow of high-risk people and the risk of infection in medical institutions, the NHIA quickly planned the "NHI MediCloud System" as a platform for medical institutions to check patients’ TOCC (Travel history, occupation, contact history, cluster) according to the instructions of the Executive Yuan and the Central Epidemic Command Center. Under the premise of personal data security, a new function of TOCC inquiry of patients is added to assist front-line medical personnel to judge infection risks and take relevant infection control measures.
(II) My Health Bank
My Health Bank was launched in 2014 on the NHIA website. Citizens can simply use the Internet and their Citizen Digital Certificate or NHI Card which has been registered to apply for My Health Bank. After their identity is verified, they can immediately search for or download their healthcare information. Users can download the past three years of their medical records and health information, including 15 categories: inpatient and outpatient data, surgery, prescriptions, allergy data, liver cancer prognosis and end stage renal disease (ESRD) evaluations, test (examination) results, preventive healthcare information, organ donation/palliative and medical care directives, adult preventive healthcare, inoculation, physiological measurements and personal radiation dose accumulated during medical examinations in the year. This system serves as a major part of policies that aim to provide healthcare and medical data to the public, for better self-health management.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, people can log in to My Health Bank to pre-order name-based masks after they complete their identity certification or mobile phone certification. Have named-based rapid test kit in 2022/4/27 and 2022/6/1.
"COVID-19 Vaccination/Testing Result " and "COVID-19 Rapid Antigen Test purchase record" was established in My Health Bank, consolidating the results of COVID-19 vaccination records, COVID-19 Rapid Antigen Tests, SARS-CoV-2 Real-time RT PCR tests, and named-based COVID-19 Rapid Antigen Test purchase record.

III. NHI Assists in Fighting COVID-19
To combat Covid-19, the Taiwan government took effective measures to investigate the source of infectious cases and contain the spread of disease. The health insurance database and the MediCloud system built over the years have become one of the important tools to help contain the epidemic. Medical institutions can exchange needed information through MediCloud system and provide relevant information for generating outbreak report. All these containing measures are implemented based on the " Communicable Disease Control Act" and " Special Act for Prevention, Relief and Revitalization Measures for Severe Pneumonia with Novel Pathogens " and aim to minimize the infringement of personal privacy and maximize the benefit of public health security.
(I) Combating COVID-19 with National Health Insurance database
1. Assisting in epidemic investigation by providing medical information
The National Health Insurance Administration provides the CECC with a daily roster for home quarantine and home isolation, a daily analysis of patients with respiratory diseases and diarrhea and the medical data analysis of home quarantine and home isolation.
2. Providing access to the National Health Insurance database for public and private sectors to jointly fight the outbreak
To share research outcomes with academic communities and the public, the NHIA has established a search portal to access journal articles based on studies using Taiwan’s NHI Database.
3. Diverting the suspected case to designated community laboratories
In order to establish a community screening network for COVID-19 and expand the capacity of medical services, the National Health Insurance Administration (NHIA) sets a new selection as a designated community laboratory on the NHI e-Referral System. With this mechanism, doctors in local clinics can rapidly help a suspected COVID-19 patient screened in community and stop suspected cases rushing to the emergency room of a hospital. This mechanism also lowers the possibilities of the spread of coronavirus in hospitals. The NHI MediCloud system will also indicate the referred case which is not screened.
According to the CECC policy, in response to the COVID-19 community pandemic, this operation has been suspended since April25, 2022 to reduce the load on grassroots institutions and public health facilities during the large-scale pandemic.
In addition, in order to track the referral of a COVID-19 case, a new item of "referral purpose" option: "COVID-19 case (including suspected) referral for treatment" can be selected for medical institutions to refer COVID-19 cases (including suspected).
4. Warning remarks in The NHI MediCloud to manage cases
The NHIA remarked travel history on people kept in home quarantine and contact remarks on people kept in home isolation in the NHI MediCloud System. Meanwhile, aircraft crew members, medical professionals, residents and workers of the residential institutions for long-term care are all put remarks in the NHI MediCloud. If these aforementioned people visit a doctor, the risk for being infected COVID-19 can be well evaluated. To encourage people to get fully vaccinated, the NHI MediCloud System provided the COVID-19 vaccination records since June 24, 2022.
According to the CECC policy, the remarks of aircraft crew members, medical professionals, residents and workers of the residential institutions for long-term care were suspended in May, 2022. Furthermore, the travel remarks on people kept in home quarantine and contact remarks on people kept in home isolation were suspended since Oct, 2022. This measure will be terminated according to the dissolution of the CECC.
5. NHI covers telemedicine to reduce the risk of exposure to coronavirus for outpatients
At the beginning of the COVID-19 outbreak, the telemedicine services were initially provided for people during home isolation, home quarantine and self-management.
When the pandemic got severe, in order to maintain medical capacity, it is critical to reduce the workload of hospitals, Considering chronic patients and the elderly are at high risk of COVID-19, starting from May 15, the designated medical institutions are allowed to use use telemedicine until the end of the Covid-19 pandemic. Furthermore, medical institutions can provide services outpatient by telemedicine without submitting a approved plan. Considering the privacy issue, doctor shall use a consultation room in a medical institution for a telemedicine. NHI covers this type of telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In response to the escalation of the pandemic in April 2022, since April 18, 2022, telemedicine care objects will be added to the confirmed cases of home care. It also simplifies the reporting procedures for telemedicine medical institutions, and people during home isolation, home quarantine and self-management can undergo telemedicine without being referred by the health bureau.
In response to the adjustment of epidemic prevention measures, medical institutions have implemented telemedicine and resumed the Rules of Medical Diagnosis and Treatment by Telecommunications since March 20, 2023. The eligible insureds are limited to “people who test positive for COVID-19 in mountainous areas and outlying islands, and residents who test positive for COVID-19 in accommodation-type long-term care institutions require oral antiviral drug treatment." It is tentatively scheduled to be implemented until April 30, 2023, and will be reviewed depending on the epidemic situation.
6. Using AI-assisted Technology to respond The COVID-19 Pandemic
National Health Insurance Administration and National Taiwan University Hospital developed “Taiwan SARS-CoV-2 Classifier” AI-pneumonia-decision-making platform to help doctors interpret CXR images immediately. As the suspected symptoms were detected by AI, the case will be quarantined at once for a rt-PCR result in order to reduce exposure risk for medical staff.
The AI-assisted alert, Med Chex, was jointly developed by the National Health Insurance Administration and the National Cheng Kung University. Med Chex can detect pneumonia from X-rays images and calculate the risk of COVID-19 within one minute. With this information, doctors can identify COVID patients instantly, and immediately to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic.
(II) Name-based Mask Distribution System
Name-based Mask Distribution System is based on the NHI card for everyone. Under the Name-based System for Mask Purchasing, people are required to use their NHI Card to purchase masks, and the date and the amount of masks will be recorded in the NHI MediCould System. People buy the masks at pharmacies named Name-based 1.0, the online purchase called Name-based 2.0 and recently making an order at the convenient store’s Kiosk called Name-based 3.0.

1. Name-based Mask 1.0: Purchase at pharmacies
The mask containment system operated through the Virtual Private Network by the NHIA, and masks are sold through NHI-contracted pharmacies and public health centers. The mask containment system is used by the NHI-contracted Pharmacies for the sale management, where people’s qualifications to buy masks, the records of the amount and date of mask purchasing will be managed. The NHIA also releases the updates on the mask stocks of every single NHI-contracted pharmacy on the NHIA website. In collaboration with Taiwanese software engineers, Minister without portfolio Ms. Audrey Tang and her partners created information platforms for open collaboration to the general public, enterprises and industries. For the first real-time map of local mask supplies to the following over 100 various applications, Ms. Tang has set a paradigm for digital solutions to combat COVID-19.
2. Name-based Mask 2.0: Online Purchase (Ceased on October 24,2021)
In order to improve the queue issue for purchasing masks at pharmacies, and to increase accessibility to masks for people aged 20 to 40 who are usually regularly employed and full-time students and account for 40% of the aforementioned age group, people can go online to buy masks with NHI Health Express APP on a cellphone, or go to eMask purchase system with the NHI card/ Citizen Digital Card and a computer to buy masks anytime and anywhere.
3. Name-based Mask 3.0: Kiosk (Ceased on October 24,2021)
In order to provide people with a more convenient way to pre-order masks, people can make an order on Kiosk with their NHI Card at the convenient stores nationwide.
(Ⅲ) virtual NHI card
In order to realize the vision of smart medical care and digital government, the National Health Insurance Administration comprehensively promoted the use of virtual health insurance cards for medical treatment in the three major fields of "home healthcare", "telemedicine" and "video consultation" in 2022, and improved the medical treatment of people in remote villages, mountainous and outlying islands, etc. Convenience, accessibility and quality of medical services; and import payment and incentive incentives to encourage institutions to use virtual health insurance cards to provide medical services.
Planning (1) According to the digital application types and characteristics of people in remote villages, indigenous peoples, and mountainous and outlying islands, conduct local digital education and training for virtual health insurance cards; (2) Propose innovative proposals for virtual health insurance cards to be used in multiple medical fields and application model development planning, (3) handle the evaluation of the benefits of digital promotion of the virtual health insurance card policy.
General public only need to download 「NHI express app」on their mobile phones, complete the virtual NHI card application, then you can showing the QR code of your mobile phone to seek medical treatment, examination ,and online payment, towards the goal of zero-touch medical treatment, and reduce the risk of people going out for medical treatment. 494,799 virtual health insurance cards had been issued as of April 30, 2023.
(Ⅳ) the NHIA had provided a subsidy helping the contracted hospitals
In 2020, the NHIA had provided a subsidy helping the contracted hospitals and clinics earning less than 80% compared with pre-COVID stage to sustain their daily operation. Since the COVID-19 pandemic is more severe in 2021, the NHIA had subsidized contracted hospitals and clinics in the same way as in 2020, with quarterly settlement to ease their financial pressure.
- Created:2020-05-14
- Last Updated:2023-05-15
- Data Source:National Health Insurance Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare
- Count Views: