Smart community transmission prevention
I. Employing NHI big data to help front-line workers detect cases:
(I) Preventing specific individuals from becoming a gap in epidemic prevention:
1. The travel history of people subjected to home quarantine is specified in the NHI-MediCloud System.
2. The contact history of people subjected to home quarantine is specified.
3. The occupation of flight crews, healthcare workers, and residents or workers at residential long-term care facilities is specified.
4. The travel history of naval crews of the Dunmu Fleet is specified.
(II)Linking related information to build smart disease prevention technology for frontline workers
1. Healthcare workers can use NHI-MediCloud system to check patients' travel history and determine if a patient is potentially infected with COVID-19 based on the patient's symptoms, so that necessary patient diversion measures can be immediately taken.
2. Medical institutions can use the electronic referral platform to upload medical information of people in home isolation or home quarantine to facilitate the judgement of infection condition.
II. Adopting technology to strengthen isolation and quarantine measures
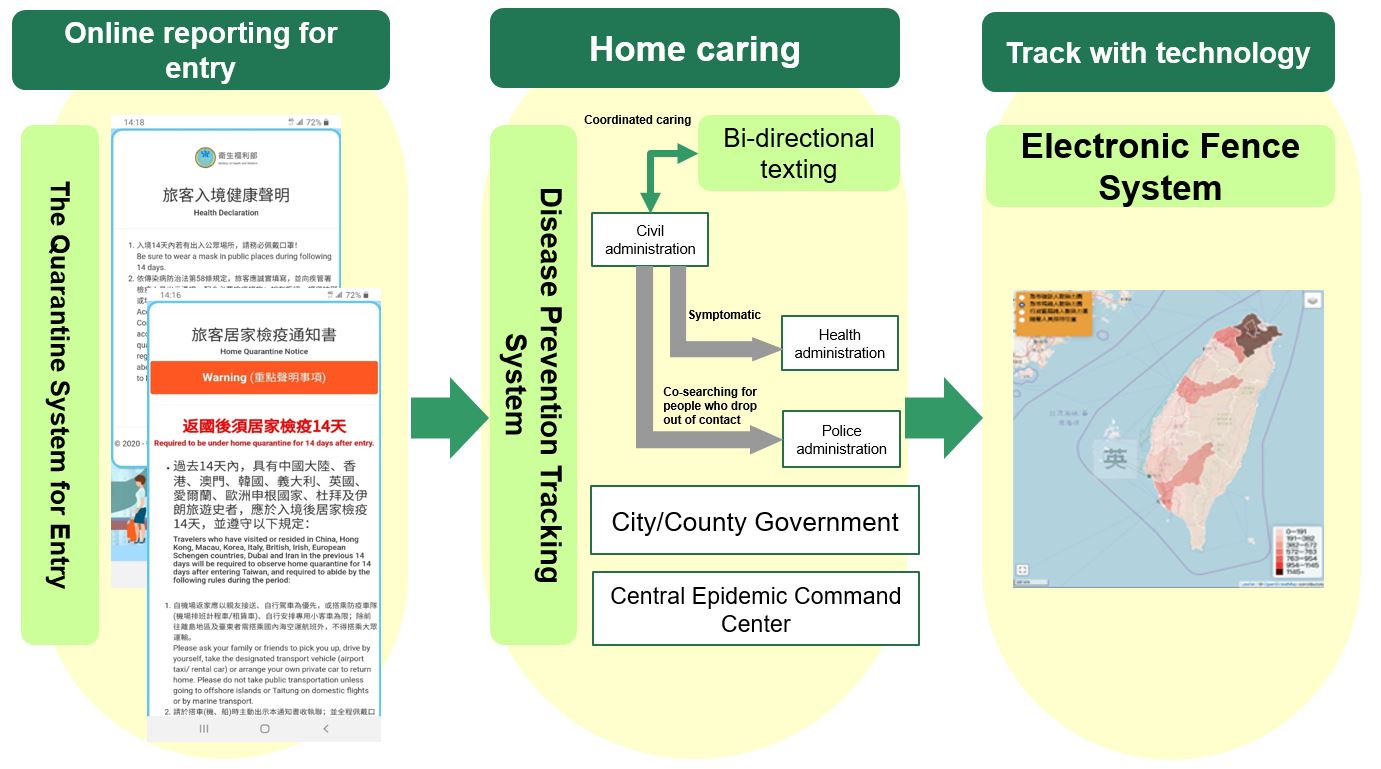
(I) Quarantine System for Entry system
1. The Quarantine System for Entry was established to accelerate the immigration process by scanning a QR Code before taking off or after landing and filling out a health declaration online.
2. Travelers’ information is integrated into the disease prevention tracking system for the 14-day quarantine, as well as the Digital Fencing Tracking System to accurately track whereabouts of people in quarantine and issue warnings.
(II) Applying technology to help enforce home isolation and home quarantine
1. Through the "Digital Fencing Tracking System ", in cooperation with telecom operators, the location of people in home isolation and home quarantine can be monitored by detecting electromagnetic signals of their mobile phone to determine whether they leave the range of their home.
2. When people in home isolation or home quarantine leave their home or turn off their mobile phone, the tracking system will send a warning message to them, as well as the civil affairs authorities, health agencies, and local police to get hold of their location.
3. For travelers who enter Taiwan without a Taiwanese phone number, a mobile phone will be provided to them, so that health officials can immediately contact them and provide assistance and care.
4. Two-way SMS messages are sent to people under quarantine and isolation on a daily basis, and they can report their health conditions back by replying to the messages they receive. Responses are separately uploaded to the Contact Follow up and Management System and Tracing System to provide accurate information for frontline workers.
5. COVID-19 contact tracing self-reporting system to be launched on May 1, 2022 to simplify contact tracing procedures of health departments.
Technology helps enforce home isolation and home quarantine.
III. Expanding telecare to reduce the risk of community spread
(I) The Health Department established a process for medical diagnosis and treatment by telecommunications, and disease prevention hotline and contact person, so that people subjected to home quarantine or home inspection can call the local Health Bureau for assistance when they require medical attention.
(II) Disease history-taking may be carried out via telecommunications and a prescription may be written for situations that require immediate medical treatment in accordance with the Rules of Medical Diagnosis and Treatment by Telecommunications.
(III) Chronic disease patients in a stable condition may ask others to describe their condition to a physician and collect a prescription, or provide services via telecare for patients with special conditions in accordance with the Rules of Medical Diagnosis and Treatment by Telecommunications.
IV. Creating a strong disease prevention network through thorough epidemiological investigations and tracking, as well as a professional decision-making team.
(I) Staying informed on international developments to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the latest status of the epidemic worldwide.
- Closely monitor updates on the epidemic worldwide from various channels, and carefully determine trends to adjust epidemic levels of all regions at any time.
- Taiwan's International Health Regulations (IHR) focal point constantly shares and exchanges crucial epidemic information or critical public health issues with the international community.
(II) Preventing the epidemic from spreading with quick and stringent disease investigations and testing
- On January 15, 2020, COVID-19 was listed as a notifiable disease; whenever a suspected case becomes a confirmed case, public health officials immediately launch an investigation, assign health workers to conduct health education, and quickly perform COVID-19 tests. Environmental cleaning and disinfection are also carried out to prevent the epidemic from spreading in an environment.
- In addition, our community surveillance system has been reinforced, and criteria for case monitoring and reporting have been expanded. Furthermore, travelers arriving from various epidemic regions at different times have been individually tracked to determine their movements. These measures have been taken to block the virus early on and prevent its spread in communities.
(III) CECC is led by a team of experts, and important decisions are based on disease prevention expertise
- The Central Epidemic Command Center (CECC) has held 22 expert consultation meetings so far. The CECC’s expert team continues to provide professional recommendations regarding disease prevention measures that need to be taken and ensure the effectiveness of disease prevention measures.
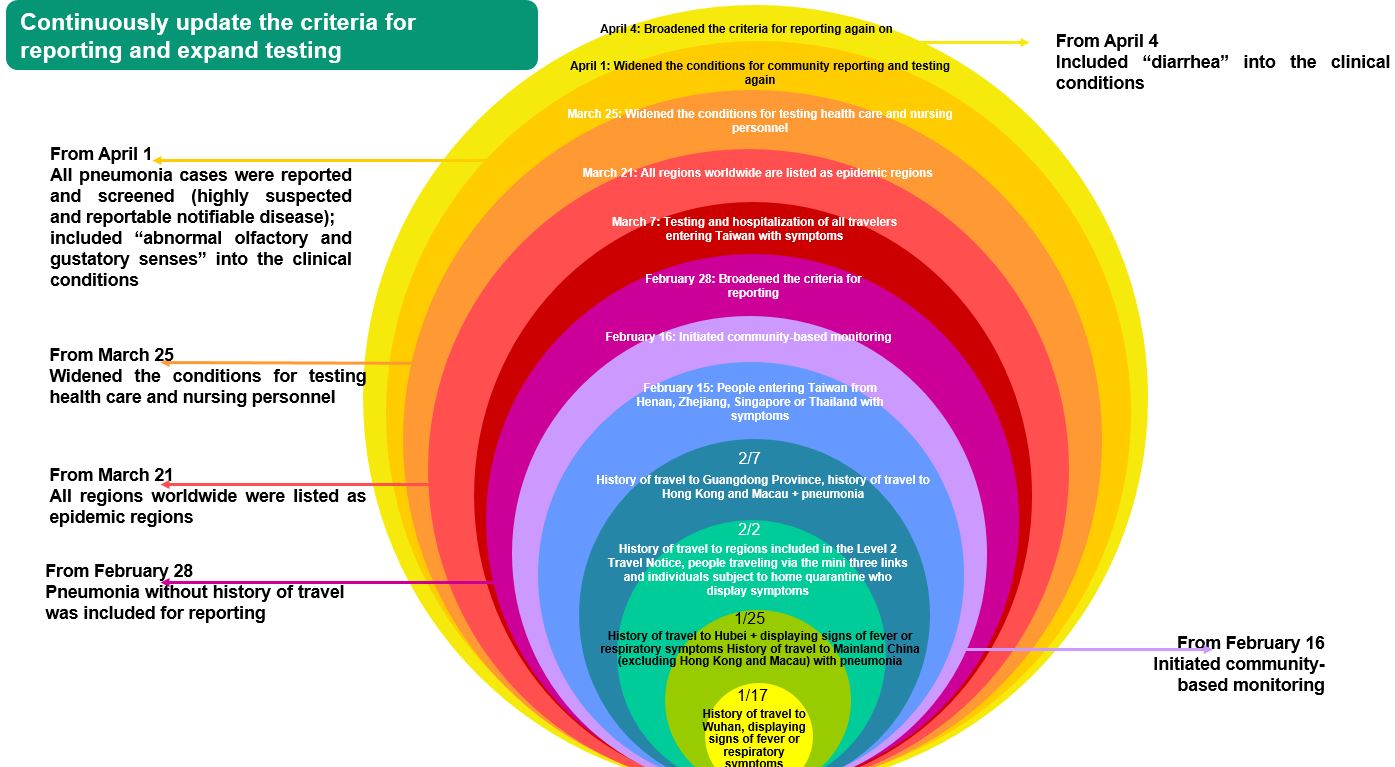
- Based on their clinical experiences and results from epidemiological investigations, the CECC’s expert team continuously adjusts case definitions and the criteria for case reporting, revises clinical and medical treatment recommendations, and shares and exchanges the latest disease prevention information with the international community.

Central Epidemic Command Center advisor Chang Shan-chwen convenes an expert consultation meeting to set criteria for COVID-19 case reporting and related medical guidelines.
The Central Epidemic Command Center adjusts criteria for COVID-19 case reporting based on the development of international and domestic situations.
- Created:2020-05-14
- Last Updated:2023-02-16
- Data Source:Centers for Disease Control, Ministry of Health and Welfare
- Count Views: